Table of Contents
Introduction
Disclaimer: This article does not replace medical advise. Please contact your Doctor for professional advise.
Welcome to our blog post on the 5 key concepts in psychopharmacology that you should know. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of psychopharmacology, exploring the essential principles and ideas that form the foundation of this field. Whether you are a student, a healthcare professional, or simply someone interested in understanding the effects of medications on the mind, this article will provide you with valuable insights. So, let’s dive in and explore the crucial aspects of psychopharmacology together.

Psychopharmacology is the scientific field that focuses on the study of how drugs affect the mind and behavior. It investigates the interaction between chemicals and the central nervous system, aiming to understand how these substances can alter our thoughts, emotions, and actions. By exploring the mechanisms of action, psychopharmacology seeks to develop a deeper comprehension of drug effects, including their therapeutic benefits and potential risks. This discipline plays a crucial role in the development of medications for various mental health disorders, such as depression, anxiety, and schizophrenia. Through extensive research and experimentation, psychopharmacologists strive to enhance our understanding of drug action and refine treatment approaches for individuals with psychiatric conditions.
Understanding Psychopharmacology
Psychopharmacology is the study of how drugs affect the human brain and behavior. It examines the interactions between various medications and the central nervous system, aiming to understand their mechanisms of action and their impact on mental health and cognitive processes. This field of study plays a crucial role in the development of effective treatments for psychiatric disorders such as depression, anxiety, and schizophrenia. By investigating the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of drugs, researchers in psychopharmacology aim to optimize drug therapies and minimize potential side effects. The knowledge gained from this discipline contributes significantly to advancements in psychological and psychiatric care, ultimately improving the well-being and quality of life for individuals affected by mental health conditions.
Pharmacodynamics refers to the study of how drugs exert their effects on the body. It examines the interactions between drugs and the biochemical processes occurring within an organism. Psychopharmacology, on the other hand, is a specific branch of pharmacology that focuses on the effects of drugs on the mind and behavior. It explores how different medications can alter brain chemistry and influence emotions, thoughts, and behaviors. Psychopharmacological research aims to understand the mechanisms by which drugs interact with the central nervous system and how these interactions can be utilized for therapeutic purposes. By studying pharmacodynamics in the context of psychopharmacology, researchers gain insights into the effects and potential applications of various medications for mental health conditions.
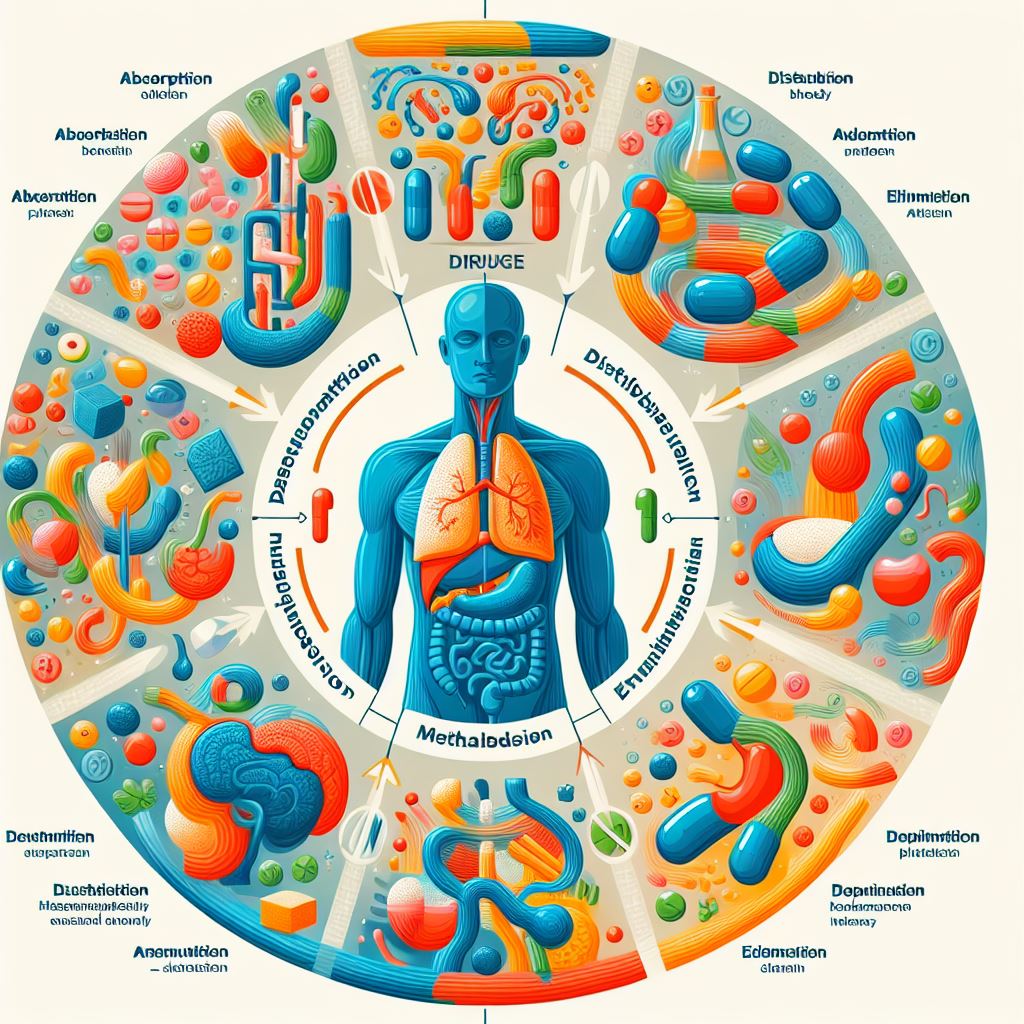
Pharmacokinetics refers to the study of how a drug is absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted by the body. It involves understanding the processes by which drugs are absorbed into the bloodstream, how they are distributed to various tissues and organs, the chemical transformations they undergo in the body, and how they are eliminated from the body. This field of study is crucial in determining the optimal dosage regimen for a particular drug, evaluating its efficacy, and predicting its potential side effects. By gaining insights into pharmacokinetics, researchers and healthcare professionals can better understand how drugs interact with the body and make informed decisions regarding drug administration and dosing strategies.
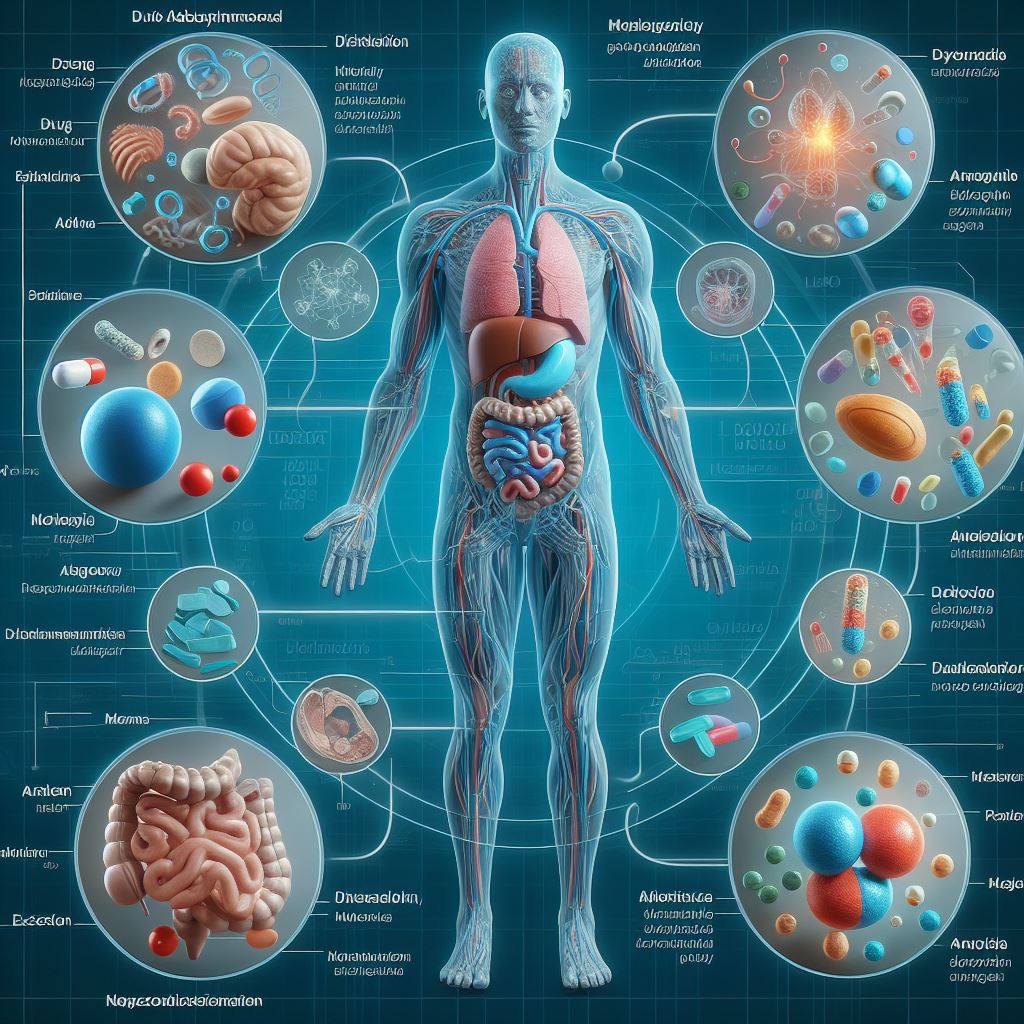
Mechanism of Drug Action
Psychopharmacology is the branch of pharmacology that focuses on the study of how drugs affect the mind and behavior. It explores the mechanisms of drug action and their impact on the central nervous system. Drugs exert their effects by interacting with specific receptors or altering the levels of neurotransmitters in the brain. Receptor interactions can be agnostic, where drugs mimic the action of endogenous neurotransmitters, or antagonistic, where drugs block the action of neurotransmitters. Additionally, drugs can affect neurotransmitter levels through processes such as re uptake inhibition or enzymatic breakdown inhibition. Understanding the mechanism of drug action is crucial for the development of effective pharmacological treatments for various mental disorders.
Mechanism of Drug Action refers to the specific processes by which drugs interact with the body to produce their therapeutic effects. Drugs can exert their actions through various mechanisms, including binding to specific receptors on cells, inhibiting enzymes, altering ion channels, or affecting intracellular signaling pathways. Receptor binding is a common mechanism, where drugs bind to specific receptors on cell surfaces, triggering a cascade of biochemical events that ultimately result in the desired therapeutic effect. Enzyme inhibition, on the other hand, involves drugs blocking the activity of specific enzymes, thereby interfering with crucial biochemical processes in the body.
Moreover medications can also regulate ion channels impacting the movement of ions through cell membranes and changing the characteristics of cells. Lastly medications might function by modifying signaling pathways interfering with or boosting communication and resulting in the intended pharmacological outcome. It is essential to grasp the ways in which drugs operate for creating secure treatments.
Resilience in Action: A Deep Dive into Stress Management Methods and their Impact
Neurotransmitters and Receptors
Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers in the brain that allow communication between neurons. They play a crucial role in regulating various physiological and cognitive processes in the body. These neurotransmitters bind to specific receptors on the surface of target cells, triggering a cascade of molecular events that ultimately result in the transmission of signals. The binding of neurotransmitters to receptors can either excite or inhibit the activity of the target cell, depending on the type of neurotransmitter and receptor involved. This intricate signaling system is essential for maintaining proper brain function and is a key focus of study in the field of psychopharmacology, which explores how drugs interact with neurotransmitter systems to influence behavior and mental processes.
Drug Classes and Effects
In this realm various drug categories are utilized, such as antidepressants, antipsychotics, anxiolytics and stimulants. For example antidepressants are used to address depression and regulate mood by acting on neurotransmitters, in the brain. Antipsychotics on the hand aid in managing symptoms of psychosis and schizophrenia by targeting dopamine receptors. Anxiolytics help alleviate anxiety and induce relaxation while stimulants are commonly employed to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) by enhancing focus and attention. A comprehensive understanding of drug categories and their effects is vital for healthcare professionals when determining the treatment strategies, for their patients.
Considerations and Side Effects
When it comes to psychopharmacology it’s important to consider factors and potential side effects. When looking at treatment options in this field it’s crucial to account for things, like the diagnosis, individual patient traits and possible drug interactions. It’s also vital to be mindful of the side effects that can come with using drugs. These side effects can range from mild and temporary to serious and lasting.
While these medications can be quite effective, in treating disorders they may also lead to effects. To tackle these issues there are approaches to consider. Firstly adjusting the medication dosage can help reduce impacts while still providing benefits. Secondly combining medications with therapy or counseling can offer support and aid in managing side effects. Moreover keeping track of patients through follow up appointments enables healthcare professionals to monitor medication effectiveness and address any side effects promptly. Making lifestyle changes like maintaining a diet exercising and employing stress relief techniques can also help minimize side effects. Lastly being knowledgeable, about the medications being used and their potential side effects empowers patients to communicate effectively with their healthcare providers and seek solutions.
Decisions regarding treatments should weigh the benefits against the risks while also keeping an eye on any adverse effects that may occur in patients. Having a grasp of considerations and side effects is key, for making informed choices in the realm of psychopharmacology.
Conclusions
The blog post explores 5 key concepts in psychopharmacology that are essential for understanding the effects of medications on the brain and behavior. By examining topics such as drug targets, pharmacokinetics, and therapeutic indications, readers gain valuable insights into the complex world of psychopharmacology. Understanding these concepts can enhance our awareness of mental health treatments and empower us to make informed decisions. Share this informative blog post on social media to spread awareness and foster conversations about psychopharmacology. Together, let’s promote a better understanding of mental health and the crucial role of psychopharmacology in it.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does psychopharmacology impact mental health treatment?
Psychopharmacology plays a vital role in mental health treatment by using medications to target specific neurotransmitters and regulate brain chemistry, helping to alleviate symptoms of mental disorders.
What are some common side effects of psychopharmacological medications?
Common side effects of psychopharmacological medications may include drowsiness, dizziness, nausea, dry mouth, weight changes, and changes in sexual function. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional about potential side effects before starting any medication.
Remember to consult with a healthcare professional or a qualified expert for personalized advice and information regarding psychopharmacology.